- Home
-
Research focus
Assessment and control of the state of green spaces according to multispectral survey data by unmanned aerial vehicles and high-resolution satellite images. Remote sensing technologies make it possible to assess the spatial structure of green spaces and their condition, including taking into account daily, seasonal and long-term dynamics. The use of modern image processing and spatial modeling technologies makes it possible to create an inventory of green spaces, build 3D models of crowns and evaluate vegetation indices. To monitor the green areas of the city of Chisinau, the project used hyperspectral images obtained with the help of a UAV equipped with an RGB camera and a multispectral complex of 5 cameras covering the blue, green, red, red and near-infrared channels of the spectrum.
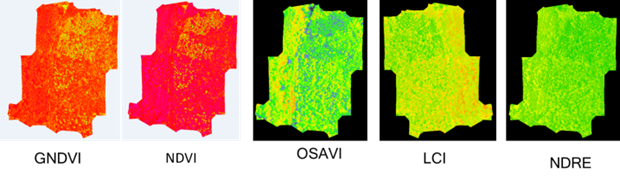
Five generally accepted vegetation indices were used to assess plant condition: NDVI, GNDVI, OSAVI, LCI and NDRE.
- NDVI (Normalized Relative Vegetation Index) - The vegetation index is calculated from the ratio of reflectances in the red and near infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. NDVI is highly correlated with primary production and biomass and is therefore considered an indicator of bioproductivity and associated system resilience. Under unfavorable conditions, the formation of chlorophyll in the leaves of trees slows down, which causes an increase in red reflectance and a decrease in the infrared region of the spectrum, which affects the NDVI value;
- GNDVI (Green Normalized Relative Vegetation Index) is an indicator of leaf and needle chlorophyll concentration, photosynthesis rate and plant stress. With yellowing and shrinking, reflectance increases in the red and decreases in the green region of the spectrum, resulting in a decrease in GNDVI values. The index is also used to identify plants of other species located in the territory;
- NDRE - (Normalized Red Edge Difference Index) - is used to determine the concentration of nitrogen in the leaves by evaluating the activity of photosynthesis;
- OSAVI - (soil vegetation index) - used to study the state of young and sparse green vegetation, taking into account the state of the soil.
- LCI - (leaf chlorophyll content index) - designed to evaluate the growth of vegetation cover and yield; serves as an indicator of nutritional deficiencies, disease, plant growth and senescence.
The better the plant feels (good cellular structure - the plant has enough nutrients, moisture, light, there are no negative factors affecting its growth) - the less the red spectrum of light is reflected from the leaf plate and the infrared spectrum closer is reflected more strongly. And vice versa, if the plant lacks nutrition, moisture, light, is affected by pests, diseases, etc., then the leaf begins to decay - the red spectrum begins to be reflected from it more strongly, and the near infrared spectrum is reflected less
Areas of application:
- Georeferencing and detailed mapping of green areas and infrastructure;
- Inventory of green spaces: evaluation of the number of plants and the contours of the crown;
- Predictive assessment of biomass by tree height and crown area;
- Calculation of leaf surface indices;
- Evaluation of the state of green plantings through vegetation indices;
- Diagnosing the state of stress of green spaces; Building 3D models of the territory.
Monitoring using UAV for practical tasks:
- Creation, preservation and care of green spaces;
- Development of a management system for green areas;
- Monitoring the state of green spaces and infrastructure.
Contacts
-
(+373 22) 77-04-47
Mon-Fri: 8:00 - 17:00
-
Republic of Moldova, Chisinau, str. Padurii, 20
-







